As an endurance athlete, you've probably heard about VO2 max. In simple terms, it's your body's ability to use oxygen.
If you want to increase your VO2 max, you need two things:
In this blog you will learn what VO2 max is and how to calculate, measure, and test VO2 max.
What is VO2 max?
VO2 max is your maximum aerobic capacity. It is the maximum amount of oxygen you can absorb from air, your maximum ability to transport oxygen to your muscle cells, and its maximum utilization in your cells.
Your VO2 max determines the upper limit of energy creation in endurance sports, and it is a gamechanger in cycling, triathlon, swimming, running, trail running, and other fast sports, such as soccer, basketball, and hockey.



Absolute
VO2 max booster


Fusion
Fat burn, VO2 max


Coenzyme Q10
Boost cellular energy



Cardio Max
Heart muscle support
What is the meaning of VO2 max?
VO2 max is one of the main parameters to measure your progress, which is why athletes try so hard to increase it. Unfortunately, this requires a lot of work.
VO2 max depends on the optimal conversion of ATP in the mitochondria. It is a basic process that acquired energy through the aerobic pathway. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) is the molecule that you use as the source of energy to fuel the processes in your body.
Your body stores around 250 grams of ATP, and to get energy, your body breaks down ATP into smaller parts, which then your metabolic enzymes use to create fuel.
 VO2 max test in progress!
VO2 max test in progress!
VO2 max calculation and formula
VO2 is expressed as the ratio between liters of oxygen per minute (L/min) or milliliters per kilogram of body mass per minute (ml/kg/min).
VO2 max is calculated following Fick's equation, which states that VO2 max equals your cardiac output multiplied by the quantity of oxygen in your blood vessels (arteries minus veins):
VO2 max = Q x (CaO2 - CvO2)
What determines VO2 max?
VO2 max is determined by several factors.
- Lung capacity (the lungs through capillaries saturate arterial blood with oxygen).
- Heart capacity (heart rate, stroke volume).
- Blood oxidative capacity (blood quantity, hemoglobin,hematocrits),
- Muscle ability to absorb oxygen (mitochondria, capillaries, oxidative enzymes).
Lung capacity
Lung capacity is the first step in the transport of oxygen into your muscles. You can determine your lung capacity with aspirometry test.
Your lung capacity also depends on your breathing technique, so you should consider doing breathing exercise.
Heart capacity
The pumping capacity of the heart is a combination of stroke volume and heart rate. The stroke volume is the volume of blood your ventricle pumps at one systole (from the left ventricle into the aorta). This increases the final diastolic volume and the amount of blood pumped from the ventricle during the systole.
Blood and oxidative capacity
Your aerobic capacity is greatly influenced by blood quantity and oxidative capacity.
Training increases the amount of blood in your body, and with correct training methods, sufficient rest, and a proper diet, your blood will have a high oxidative capacity.
Pulmonary capillaries transfer oxygen and CO2 through erythrocytes to the mitochondria. At erythrocyte level, we are mostly interested in hemoglobin levels (oxygen binds to hemoglobin). Of secondary importance are hematocrit levels (the percentage of erythrocytes in the whole blood volume), measurement of red blood cell size (MCV), average amount of hemoglobin in a red blood cell (MCH), average concentration of hemoglobin in a red blood cell (MCHC), and iron values.
Iron is mostly found in hemoglobin. In case of iron deficiency and before races, but without medical supervision only for a brief period of time, you can supplement it with a high-bioavailability iron supplement.
Muscle capacity
High upper limits are not enough if your muscles are unable to intake the oxygen. This is called muscle oxidative capacity. Muscle oxidative capacity depends on the density of the capillary network in the muscles, the number of mitochondria, and the activity of oxidative enzymes.
If a test reveals issues in this area, you must address this issues in your training routine.
How to measure VO2 max at home?
VO2 max can be precisely measured with graded exercise testing by using measurement equipment to measure pulmonary gas exchange (VO2 / VCO2). Since we usually don't have this equipment at home, we can use various tests to calculate VO2 max.
Don't get scared, these equations are not as complicated as they seem.
Graded exercise testing
One of the most used is graded exercise testing. The main focus is power (W) at the final stage (PPO – peak power output).
Use this equation to calculate your VO2 max:
VO2 max [ ml/kg/min ] = (10,8 x P/m) +7
where P equals power (watt), and m equals body mass (kg).
Depending on your efficiency, the calculated values can range from -5% to +5%.
VO2 max can be expressed in absolute terms in liters of oxygen uptake per minute (L/min). This way everyone can calculate how much energy they are able to create: 1 liter of oxygen uptake creates approximately 5 kcal or 21 kJ of energy.
Balke 15-minute test for runners
One of the most useful methods for runners is Balke 15-minute test. Balke test consists of running for 15 minutes as fast as possible and write down the distance traveled (to the closest 25 meters).
Use this equation to calculate your VO2 max:
VO2 max [ ml/kg/min ] = ((m/15-133) x 0,172)) + 33,3
where m equals meters traveled.
 Absolute is a natural supplement to improve VO2 max based on high-quality adaptogens and beta-alanine.
Absolute is a natural supplement to improve VO2 max based on high-quality adaptogens and beta-alanine.
VO2 max values
There is a difference of opinions about VO2 max. Some athletes believe it all comes down to genetics, others believe it can be improved with training.
Since your VO2 max values depend on several factors, it can definitely be improved, but in our experience it is true that some athletes need to work a lot harder to reach the recommended values than others.
For cyclists, a VO2 max of 70 ml/km/min is generally considered to be too low for the professional level. In sports that include more muscles, the VO2 max values are even higher. On the other hand, the VO2 max values of female athletes are generally 20 to 30% lower.
Your VO2 max values are greatly influenced also by your anaerobic threshold. The anaerobic threshold is the point at which, due to the lack of oxygen in ATP production, byproducts are produced (hydrogen ions and lactate), which quickly leads to fatigue.
If your anaerobic threshold is at a low percentage of your VO2 max, your performance might be inferior to athletes with less endurance but an anaerobic threshold at a higher percentage of their VO2 max, even if their VO2 max is lower than yours.
The anaerobic threshold of professional and top-level cyclists is from 85 to 90% of VO2 max, and at 70 to 80% for less trained athletes.
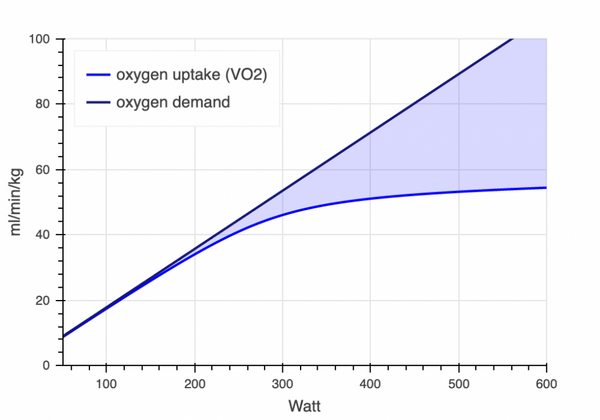 VO2 max does not tell the whole story. You must also compare your VO2 max to VLamax (the maximal lactate production rate) and determine whether your anaerobic or aerobic metabolism (glycolytic gap) is more developed. Unless you test both aspects that affect your endurance, it is difficult to assess which area needs to be improved.
VO2 max does not tell the whole story. You must also compare your VO2 max to VLamax (the maximal lactate production rate) and determine whether your anaerobic or aerobic metabolism (glycolytic gap) is more developed. Unless you test both aspects that affect your endurance, it is difficult to assess which area needs to be improved.
All this information helps you to calculate your power at the anaerobic threshold. Then you can tweak different values to determine what you need to change and improve to reach the desired goal.



Absolute
VO2 max booster


Fusion
Fat burn, VO2 max


Coenzyme Q10
Boost cellular energy



Cardio Max
Heart muscle support
How to calculate power at the anaerobic threshold
Let's take a cyclist with a body mass of 65 kg, a VO2 max of 75 ml/kg/min, with anaerobic threshold at 90% VO2 max, and 23% efficiency. You will see what "efficiency" means from the equation below.
75 ml/kg/min x 65 kg = 4,88 L/min (absolute VO2 max)
4,88 L/min x 90% = 4,39 L/min (absolute VO2 max at anaerobic threshold)
At this point we get to efficiency. It is how much power a cyclist is able to develop from 1 liter of oxygen or what percentage of the available energy you are able to use.
An average cyclist is able to utilize from 21 to 23% of energy, which means they can produce from 75 to 85W with 1 liter of oxygen. The rest of the energy is used by the body to function and transform energy into ATP, and more energy is lost as excessive heat.
In the end you multiply your absolute VO2 max with the consumption of energy per liter to obtain the familiar W/kg unit.
4,88 L/min x 85W = 415W / 6,38 W/kg
These calculations show that to obtain top-level results, you need:
- high VO2 max,
- anaerobic threshold at a high percentage of VO2 max,
- high efficiency in transforming energy.
VO2 max chart - normative data
The following two charts include the ranked values of VO2 max in ml/kg/min.
The numbers in the first row represent your fitness level.
1 – very bad
2 – bad
3 – satisfactory
4 – good
5 – very good
6 – excellent
VO2 max values for men:
| Age | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 13-19 | < 35.0 | 35.0-38.3 | 38.4-45.1 | 45.2-50.9 | 51.0-55.9 | > 55.9 |
| 20-29 | < 33.0 | 33.0-36.4 | 36.5-42.4 | 42.5-46.4 | 46.5-52.4 | > 52.4 |
| 30-39 | < 31.5 | 31.5-35.4 | 35.5-40.9 | 41.0-44.9 | 45.0-49.4 | > 49.4 |
| 40-49 | < 30.2 | 30.2-33.5 | 33.6-38.9 | 39.0-43.7 | 43.8-48.0 | > 48.0 |
| 50-59 | < 26.1 | 26.1-30.9 | 31.0-35.7 | 35.8-40.9 | 41.0-45.3 | > 45.3 |
| 60+ | < 20.5 | 20.5-26.0 | 26.1-32.2 | 32.3-36.4 | 36.5-44.2 | > 44.2 |
VO2 max values for women:
| Age | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 13-19 | < 25.0 | 25.0-30.9 | 31.0-34.9 | 35.0-38.9 | 39.0-41.9 | > 41.9 |
| 20-29 | < 23.6 | 23.6-28.9 | 29.0-32.9 | 33.0-36.9 | 37.0-41.0 | > 41.0 |
| 30-39 | < 22.8 | 22.8-26.9 | 27.0-31.4 | 31.5-35.6 | 35.7-40.0 | > 40.0 |
| 40-49 | < 21.0 | 21.0-24.4 | 24.5-28.9 | 29.0-32.8 | 32.9-36.9 | > 36.9 |
| 50-59 | < 20.2 | 20.2-22.7 | 22.8-26.9 | 27.0-31.4 | 31.5-35.7 | > 35.7 |
| 60+ | < 17.5 | 17.5-20.1 | 20.2-24.4 | 24.5-30.2 | 30.3-31.4 | > 31.4 |
VO2 max charts taken from: Heyward HV, The Physical Fitness Specialist Certification Manual, 3rd ed. The Cooper Institute for Aerobics Research, Dallas TX. 1998; p. 48.



Absolute
VO2 max booster


Fusion
Fat burn, VO2 max


Coenzyme Q10
Boost cellular energy



Cardio Max
Heart muscle support


